What is the essence of innovation? Throughout history, numerous events have reshaped the world, all stemming from innovative efforts. Whether it's the inception of the internet or the introduction of the first iPhone, these breakthroughs underscore the critical role that innovation plays in unlocking long-term success.
For financial institutions (FIs), this becomes even more salient with the dynamic demands of the financial industry. According to Forbes, about 80% of companies view innovation as a critical focus area within their business operations. In addition, about 60% anticipate a surge in innovation endeavours over the next 3 years. Despite the awareness, there’s a big gap in execution, and only 4% of these businesses have established a formalised process to drive continuous improvement. To navigate this landscape successfully, FIs must integrate a robust commitment for innovation.
In this article, we define what exactly it means to innovate and how FIs can leverage on innovation for success.
Overview:
- What is innovation and why is it important?
- The Importance of innovation for Financial Institutions
- The 4 types of Innovation
- Elements of Innovation / Ingredients of Innovation
- Tips for innovation / Creating a culture of successful Innovation
What is innovation and why is it important?
Innovation refers to the process of introducing new and improved ideas or products to bring about positive change.
Contrary to popular belief, innovation is not limited to groundbreaking technological advancements but also extends to creative solutions, novel business models, and improvements in processes.
The Importance of Innovation for Financial Institutions
Innovation becomes particularly important for those within the banking and fintech sector as these industries operate in a highly regulated and competitive environment. Thus, the ability to adapt to market changes, regulatory requirements, and evolving customer expectations becomes crucial in achieving long-term growth.
A study on the top Fortune500 companies revealed that 80% actively innovate through their participation in hackathons, with fintech companies leading at 23.1%.
FIs that fail to innovate risk becoming obsolete, lose market share, and fall further behind their more agile competitors. As such, innovation is not just a strategic choice; it's a strategy for survival.
Innovation Matrix: 4 Types of Innovation
To successfully innovate, one has to first know exactly the problem that we are solving for, by defining the problem statement.
This can be achieved using a strategy tool, the innovation matrix. Business leaders can use this framework to identify, align and rank priorities of innovation opportunities within their organisations.
The matrix is made up of these 2 axes:
- Impact on the market
- Technology newness
This creates an innovation matrix that produces 4 types of innovation: Architectural, Disruptive, Incremental and Radical.
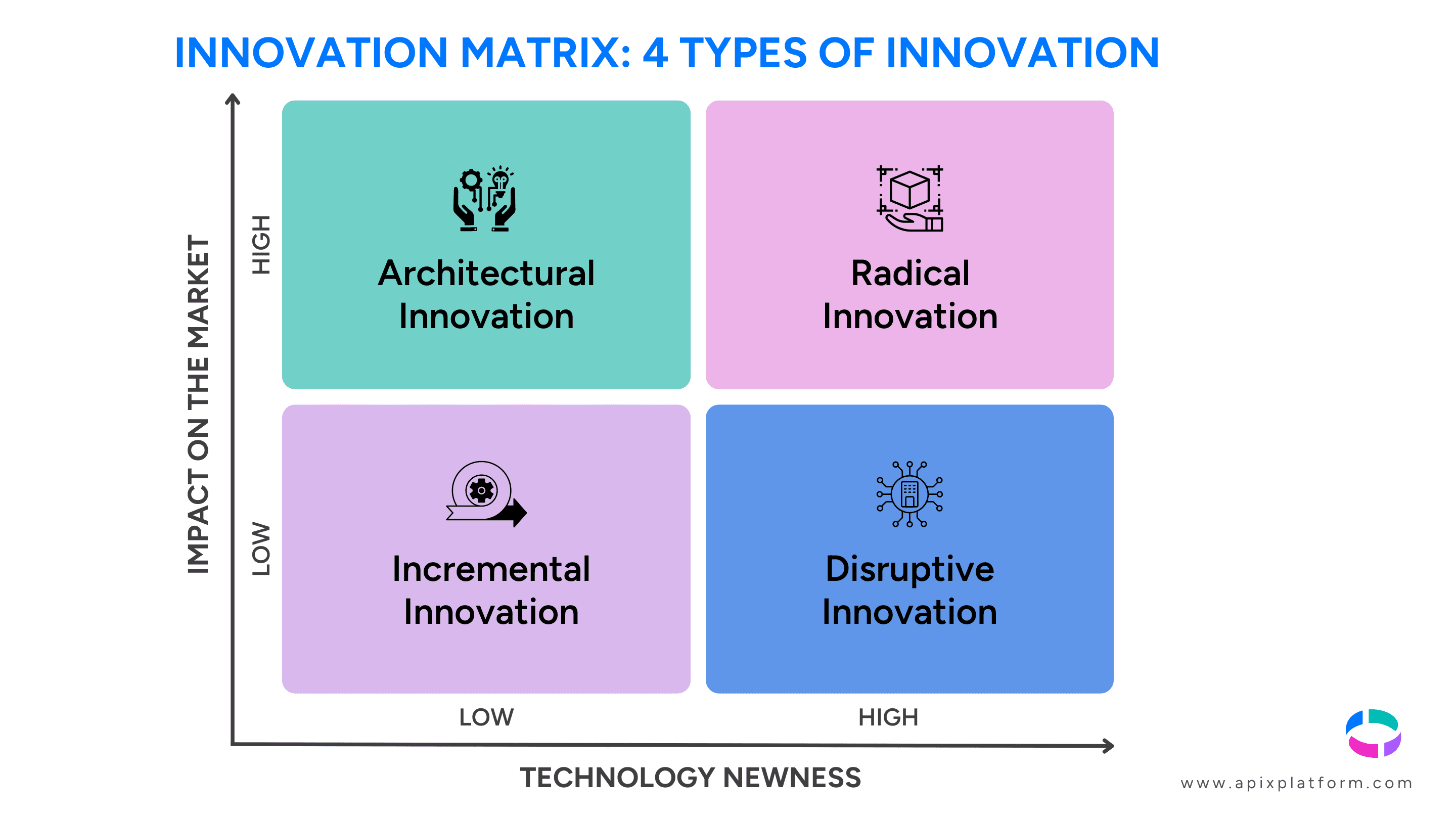
Architectural innovation
Architectural innovation relates to significant improvements that leverage current technology with the goal of reaching new segments of customers within the existing market. This innovation typically includes modifying an existing product, by using the design elements and using them in a novel way, to reach new customers. Although the components are modified or the use cases are different, the main technologies are not modified. There is a high impact on the market, however new technology isn’t needed.
An example of architectural innovation is: the multi-core processor that combined single-core processors for enhanced performance with low power performance.
Disruptive innovation
Disruptive innovation aims to radically and profoundly change an industry, by introducing completely new ways of doing something or offering a brand new service to the existing market, displacing competitors and significantly impacting business models as a result. It ranks high on technology newness.
Some examples of disruptive innovation are: video streaming services, with the advent of Netflix, and open-source software.
There are primarily two categories of disruptive innovation:
- Low-end disruption: This occurs when a company adopts a low-cost business model to penetrate the bottom of an existing market.
- New-market disruption: In this scenario, a company establishes and captures a new segment within an existing market by addressing the needs of an underserved customer base.
Typically, these two forms of disruptive innovation are intertwined, unfolding as part of a cohesive process.
An example of this is the recent introduction of blockchain technology that has facilitated the rise of digital currencies such as Bitcoin and revolutionised the world of fintech and decentralised finance (DeFi).
Incremental innovation
Incremental innovation, also known as continuous improvement, occurs when existing technology is improved upon within the market. As the name suggests, ongoing improvement of existing products, services or processes are made, thereby offering enhanced value to its customers. This causes it to be low on the impact to market and technology newness criteria, however it is still very effective.
Many business leaders, heads of innovation and digital transformation use this framework to address transformation challenges within their organisation, due to its collaborative approach.
An example of incremental innovation in action is the smartphone, and brands’ improvements in their smartphone cameras (Apple’s iPhone and Samsung). Many banks have also been using traditional AI in their banking processes in incremental innovation: some common AI applications include automation of client authentication and document processing, customer analytics, risk management scoring and chatbots.
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation, also called a breakthrough or revolutionary innovation, refers to when a novel and brand-new product is introduced to the market, sparking a demand that was previously nonexistent. It is a big idea that transforms the way a company works, and opens new markets, hence it is high on both the technology and market axis.
While not a common occurrence, breakthrough innovation is more likely to flourish in well-supported environments. While the release of Apple’s iPhone 15 is an example of sustaining innovation, the release of the very first iPhone back in 2007 is a prime example of a breakthrough innovation. Other examples include: Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI), electric vehicles (EV) and cloud-based technology.
The Elements of Innovation
Innovation is not just about disruption or technology, but also about changing an organization's culture, necessitating a shift in mindset and practices across the entire company to foster creativity and adaptability.
The Secret Sauce to Successful Innovation
Unlock innovation by hosting hackathons and open innovation challenges. These events unite diverse talents to collaboratively solve real-world issues with technology and creativity. This brings numerous benefits to financial firms, leading to transformative solutions for business problems.
With APIX, launching a global innovation challenge or hackathon becomes a streamlined process that can be set up in just hours.
Eager to start your innovation journey? Partner with APIX: we are here to help you streamline and accelerate your innovation journey.
Schedule a call with our experts to find out more.
